[HackerRank] Left Rotation / Dynamic Array
2021. 7. 14. 13:57
알고리즘
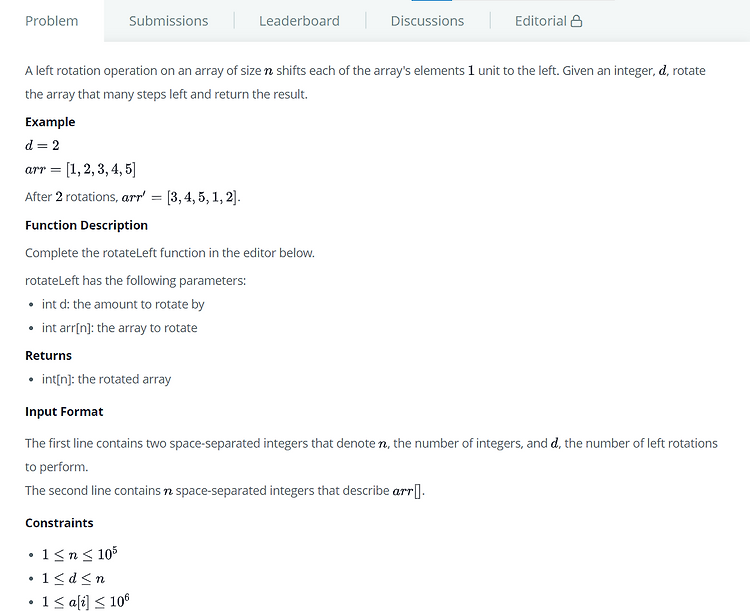
# Left Rotation (Arrays) [문제] [코드] vector rotateLeft(int d, vector arr) { vector result(arr.size()); int i, j; for(i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { j = (i+d) % arr.size(); result[i] = arr[j]; } return result; } [코드설명] 주어진 array를 left rotate 연산하는 문제다. arr내에서 해결하지 않고 추가 배열을 사용해서 해결했다. arr와 동일한 크기의 result 벡터를 만들었다. result 벡터에 arr 벡터의 값을 복사하기 위해 for 반복문으로 벡터의 크기만큼 반복하도록 했다. result의 첫 번째 인덱스부터 값을 채우려고 했..

[HackerRank] Jesse and Cookies / Insertion Sort - Part 1
2021. 7. 9. 03:40
알고리즘
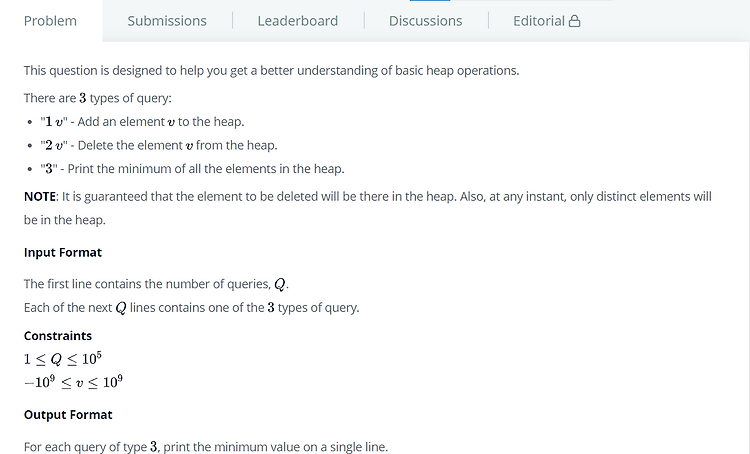
# Jesse and Cookies (Heap) [문제] [코드] void insert_heap(int item, int *heap, int *n) { int i; i = ++(*n); while((i != 1) && item < heap[i/2]) { heap[i] = heap[i/2]; i /= 2; } heap[i] = item; } int delete_heap(int *heap, int *n) { int child, item, temp; item = heap[1]; temp = heap[(*n)--]; child = 2; while(child heap[child+1])) child++; if(temp 1) { result++; num1 = delete_heap(B, &A_count); num2 =..
[HackerRank] QHEAP1 / Quicksort 1 - Partition
2021. 6. 27. 03:38
알고리즘
# QHEAP1 (Heap) [문제] [코드] #include #include #include #include typedef struct { int *arr; int total_node; } Heap; void init_heap(Heap * heap, int n) { heap->arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 1)); heap->total_node = 0; } void insert_heap(Heap *heap, int data) { int i; i = ++(heap->total_node); while ((i != 1) && (data arr[i / 2])) { heap->arr[i] = heap->arr[i / 2]; i /= 2; } heap->arr[..
[HackerRank] Tree: Level Order Traversal / Binary Search Tree : Insertion
2021. 6. 26. 12:47
알고리즘
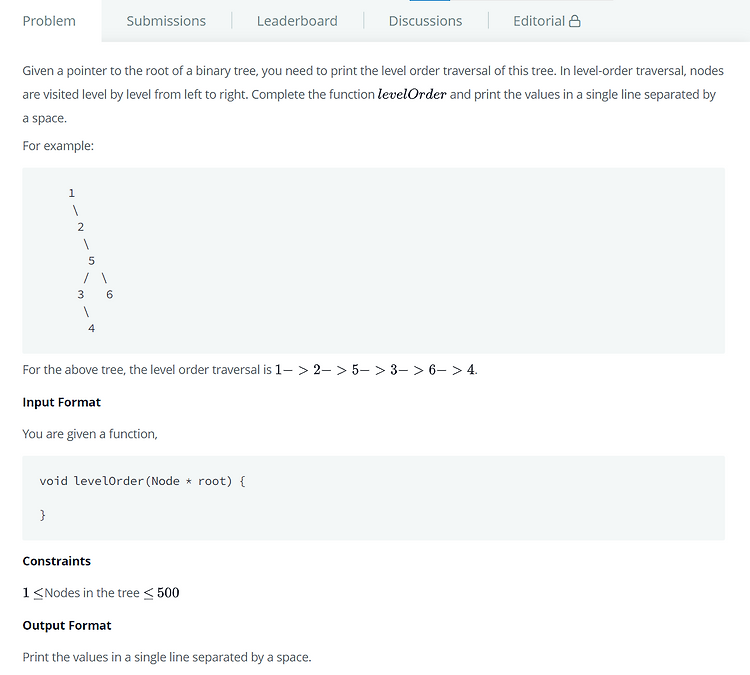
# Tree: Level Order Traversal (Trees) [문제] [코드] struct node* queue[500]; int front = -1, rear = -1; void addq(struct node* node) { queue[++rear] = node; } struct node* deleteq() { return queue[++front]; } void levelOrder(struct node *root) { struct node* temp; if(!root) return; addq(root); while(1) { temp = deleteq(); if(!temp) break; printf("%d ", temp->data); if(temp->left) addq(temp->left); i..
[HankerRank] Tree: Postorder Traversal / Maximum Element
2021. 5. 28. 15:54
알고리즘
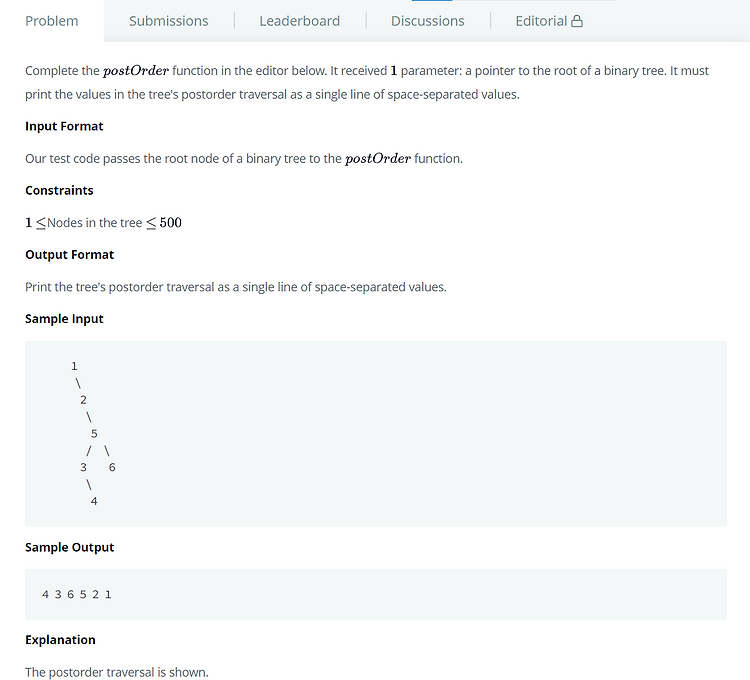
# Tree: Postorder Traversal (Trees) [문제] [코드] void postOrder(struct node *root) { if(root) { postOrder(root->left); postOrder(root->right); printf("%d ", root->data); } } [코드설명] 재귀적 호출로 해결했다. 왼쪽 노드와 오른쪽 노드로 순차적으로 내려간 다음, 다시 올라오면서 노드의 data를 출력한다. [채점 결과] # Maximum Element (Stacks) [문제] [코드] int stack[100000]; int top = -1; void push(char *item) { char ch; int val = 0; if (top == 99999) return; fo..
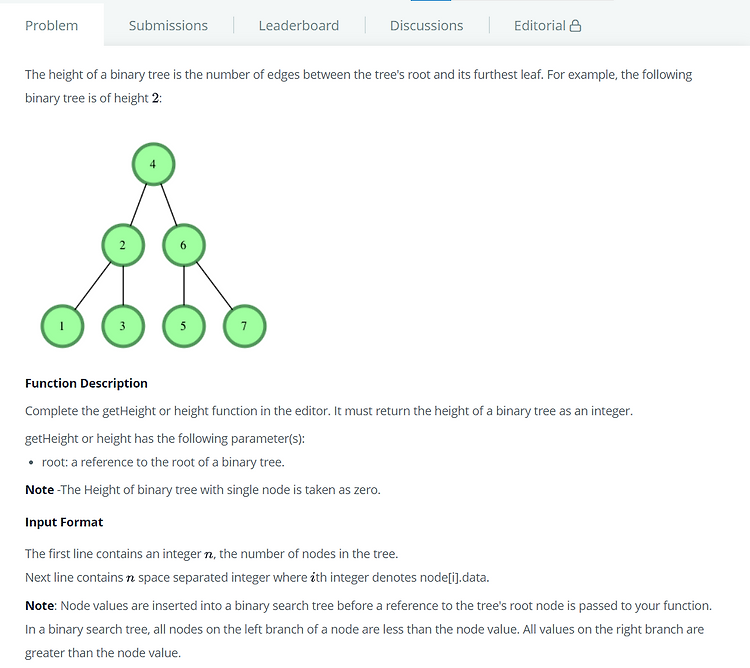
[HackerRank] Tree: Height of a Binary Tree / Tree: Inorder Traversal
2021. 5. 20. 23:14
알고리즘
# Tree: Height of a Binary Tree (Trees) [문제] [코드] int getHeight(struct node* root) { // Write your code here int left, right, height; if(root == NULL) return -1; left = getHeight(root->left); right = getHeight(root->right); height = (left > right ? left : right) + 1; return height; } [코드설명] Divide And Conquer 방식으로 해결했다. 각각 left와 right로 분할해서 각각의 height를 구하고, 두 값을 비교하여 더 큰 값에 1을 더하여 height에 저장한다. ..

[HankerRank] Reverse a linked list / Tree: Preorder Traversal
2021. 5. 14. 20:29
알고리즘
# Reverse a linked list (Linked List) [문제] [코드] SinglyLinkedListNode* reverse(SinglyLinkedListNode* llist) { SinglyLinkedListNode* two=NULL, *three; while (llist) { three=two; two=llist; llist=llist->next; two->next=three; } return two; } [코드설명] llist : 다음 노드를 가리킴two : link를 변경할 노드three : 변경할 link의 값 llist는 다음 노드를 가리킨다. three와 two는 llist를 따라 다음 link로 움직인다. 다음 노드로 이동할 때마다 노드의 link를 반대로 연결해주어야 한다...

[HackerRank] Insert a node at the head of a linked list / Missing Numbers
2021. 5. 9. 02:25
알고리즘
# Insert a node at the head of a linked list (Linked List) [문제] [코드] SinglyLinkedListNode* insertNodeAtHead(SinglyLinkedListNode* llist, int data) { SinglyLinkedListNode* node = (SinglyLinkedListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SinglyLinkedListNode)); node->data = data; node->next = llist; llist = node; return llist; } [코드설명] node: 새로 추가할 node 동적할당 node의 data 필드에 data 저장.node의 next 필드에 llist(head pointer) 저장..

[HackerRank] Print the Elements of a Linked List / Insert a Node at the Tail of a Linked List
2021. 4. 11. 14:15
알고리즘
# Print the Elements of a Linked List (Linked Lists) [문제] [코드] void printLinkedList(SinglyLinkedListNode* head) { SinglyLinkedListNode* temp; temp = head; while(temp){ printf("%d\n", temp->data); temp = temp->next; } } [코드설명] temp: LinkedList를 head부터 NULL까지 탐색할 포인터 temp가 NULL일 경우 while문을 종료한다. NULL이 아닐 경우 temp가 가리키고 있는 node의 data value를 출력한다. temp를 다음 노드의 포인터로 바꿔준다. List의 마지막에 이르면 temp가 NULL로 바뀌..